Last modified: Jan 31 2026 at 10:09 PM • 5 mins read
Supervised Learning with Neural Networks
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Real-World Applications of Supervised Learning
- Key to Success: Choosing the Right Input and Output
- Types of Neural Network Architectures
- Structured vs. Unstructured Data
- Summary
Introduction
Neural networks have generated significant excitement, and much of this enthusiasm is justified given their impressive performance. However, almost all economic value created by neural networks comes from one type of machine learning: supervised learning.
What is Supervised Learning?
In supervised learning, you have:
- Input ($x$): Features or data you provide
- Output ($y$): Target value you want to predict
- Goal: Learn a function that maps $x \to y$
Example: In the housing price prediction we saw earlier, you input features of a home ($x$) to predict its price ($y$).
Real-World Applications of Supervised Learning
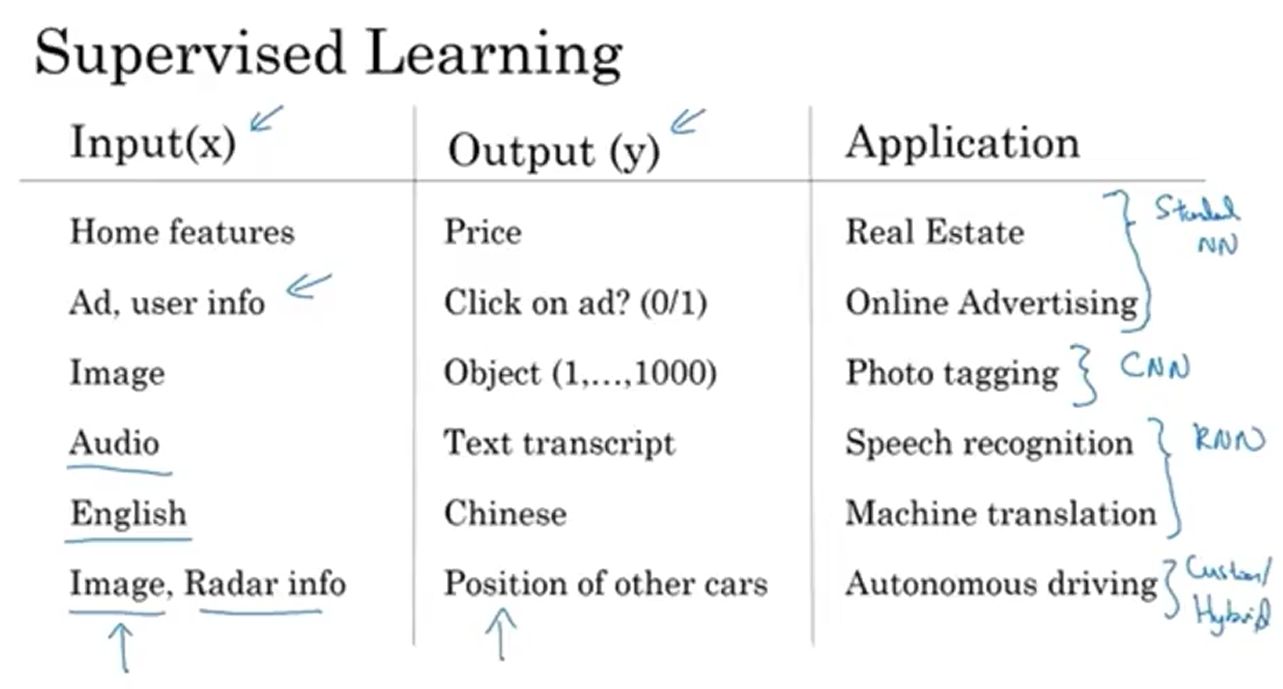
1. Online Advertising
Input ($x$): Ad information + User information
Output ($y$): Probability user clicks on the ad (0 or 1)
- Currently the most lucrative application of deep learning
- Neural networks predict which ads users are most likely to click
- Showing personalized ads has a direct impact on revenue for major companies
- The ability to show relevant ads drives the bottom line of large online advertising platforms
2. Computer Vision
Input ($x$): Image
Output ($y$): Classification (e.g., 1 of 1,000 categories)
- Huge strides in recent years due to deep learning
- Applications: Photo tagging, object recognition
- Can identify and categorize images with high accuracy
3. Speech Recognition
Input ($x$): Audio clip
Output ($y$): Text transcript
- Exciting progress in converting speech to text
- Powers voice assistants and transcription services
- Neural networks can accurately transcribe spoken words
4. Machine Translation
Input ($x$): Text in one language (e.g., English)
Output ($y$): Text in another language (e.g., Chinese)
- Neural networks can directly translate between languages
- Made huge strides thanks to deep learning
- End-to-end translation without intermediate steps
5. Autonomous Driving
Input ($x$): Image from car camera + Radar information
Output ($y$): Positions of other cars on the road
- Key component in self-driving car systems
- Combines multiple input sources for decision-making
- Fits into a larger autonomous vehicle system
Key to Success: Choosing the Right Input and Output
Much of the value creation in neural networks comes from cleverly selecting what should be $x$ and what should be $y$ for your specific problem. The supervised learning component then integrates into a larger system (like an autonomous vehicle).
Types of Neural Network Architectures
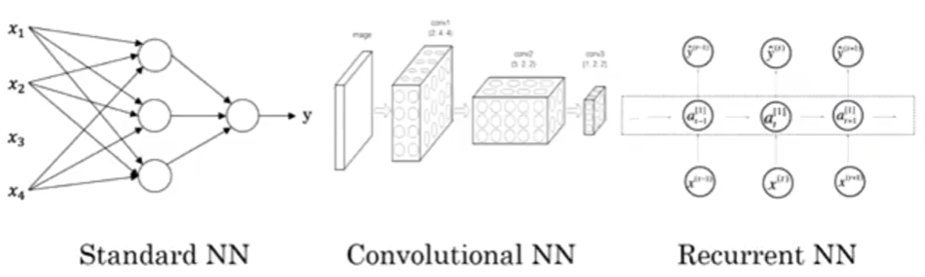
Different applications benefit from different neural network architectures:
Standard Neural Networks (Fully Connected)
Used for: Real estate, online advertising, general tabular data
- Also called feedforward networks
- Each layer connects to the next in sequence
- What we saw in the housing price example
- Works well with structured, tabular data
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Used for: Image applications
- Specially designed to process grid-like data (pixels in images)
- Efficient at recognizing visual patterns and spatial hierarchies
- Powers computer vision applications
- We’ll cover implementation details in a later course
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Used for: Sequence data (audio, text, time series)
Why sequence data?
- Audio: Has a temporal component - sound plays out over time
- Naturally represented as a 1D temporal sequence
- Language: Words/characters come one at a time
- Text is inherently sequential
- Both English and Chinese process one element at a time
More complex versions of RNNs (like LSTMs and GRUs) are commonly used for these applications. You’ll learn how to implement these in a later course.
Hybrid/Custom Architectures
Used for: Complex applications like autonomous driving
For applications with multiple input types:
- Image data → CNN component
- Radar data → Different processing component
- Combined into a custom or hybrid neural network architecture
Structured vs. Unstructured Data
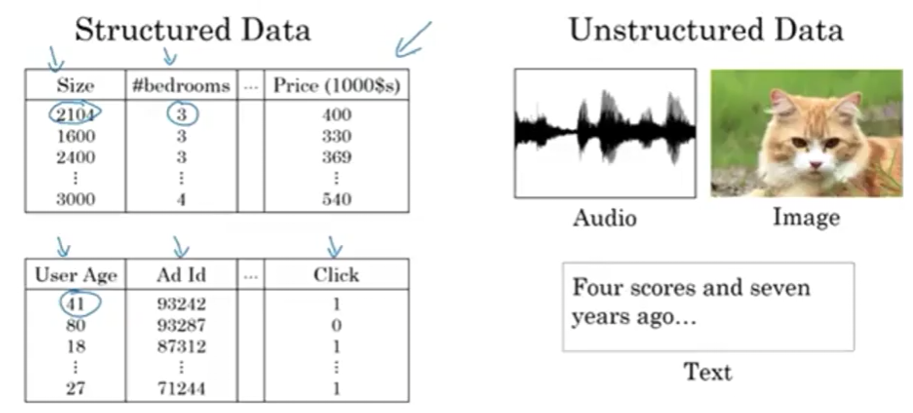
Neural networks excel at both types of data:
Structured Data
Definition: Organized databases with well-defined features
Examples:
- Housing price prediction: Database with columns for size, number of bedrooms
- Online advertising: User age, ad information, labels ($y$) to predict
- Characteristics: Each feature has a clear, well-defined meaning
Format: Tables, spreadsheets, relational databases
Unstructured Data
Definition: Data without predefined structure or organization
Examples:
- Audio: Raw audio waveforms
- Images: Pixel values
- Text: Individual words or characters
Key Challenge: Features (like pixel values or words) don’t have obvious predefined meanings
Historical Context
Before Neural Networks:
- Computers struggled with unstructured data
- Humans evolved to excel at understanding audio, images, and text
- Much easier for computers to process structured data
With Neural Networks:
- Computers are now much better at interpreting unstructured data
- Dramatic improvement compared to just a few years ago
- Creates opportunities for new applications:
- Speech recognition
- Image recognition
- Natural language processing
Economic Impact
Media Coverage: You often hear about successes with unstructured data (e.g., “neural network recognizes a cat”) because:
- People naturally understand these accomplishments
- It’s relatable and exciting
- We have empathy for interpreting images and sounds
Business Value: However, significant short-term economic value comes from structured data:
- Better advertising systems
- Improved product recommendations
- More accurate predictions from large corporate databases
- Processing giant datasets that companies already have
Course Focus
In this course:
- Techniques apply to both structured and unstructured data
- Examples will draw more on unstructured data for explaining algorithms
- As you apply neural networks, consider uses for both data types in your work
Summary
Neural networks have transformed supervised learning and created tremendous economic value through:
- Correctly identifying input ($x$) and output ($y$) for your problem
- Choosing the appropriate neural network architecture
- Integrating the model into a larger system
- Applying techniques to both structured and unstructured data
| Application Type | Input Type | Data Structure | Recommended Architecture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | Tabular features | Structured | Standard NN |
| Online Ads | User/Ad data | Structured | Standard NN |
| Photo Tagging | Images | Unstructured | CNN |
| Speech Recognition | Audio | Unstructured | RNN |
| Machine Translation | Text | Unstructured | RNN |
| Autonomous Driving | Images + Radar | Mixed | Hybrid/Custom |
Key Insight: While the basic technical ideas behind neural networks have been around for decades, recent advances have made them incredibly effective at creating economic value across diverse applications.